What are Critical Raw Materials?
The “Critical Raw Materials” Group will be listed in the Global Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL, on www.GADSL.org) from February 2021 and requiring these substances to be reported in IMDS datasheets. IMDS data contains CRM will populate in 2021 and it will mandatorily be reporting in 2022.
Metals, minerals, and natural materials are the raw materials that are part of our daily life and these raw materials that are most important economically but have a high supply risk are called critical raw materials. Critical raw materials are essential to the functioning and integrity of a wide range of industrial ecosystems. For example, Tungsten makes phones vibrate, Gallium and indium are part of light-emitting diode (LED) technology in lamps, Semiconductors need silicon metal, and Hydrogen fuel cells and electrolyzers need platinum group metals.
The EU Commission has identified in several communications, including the Waste Framework Directive, the new Battery Regulation, or the Circular Economy Action Plan that a more robust approach is needed in the management and recovery of critical raw materials. They expect industries to know where these materials are used and to use these materials responsibly. Recycling and recovery targets for producers as well as labeling obligations are also on the strategic landscape. So, the Commission is committed to updating the list every 3 years to reflect the production, market, and technological developments.
The list has been prioritized based on the EU Commission’s critical assessment those substances defined as very high, high and moderate, were chosen in the definition in the development of this list.
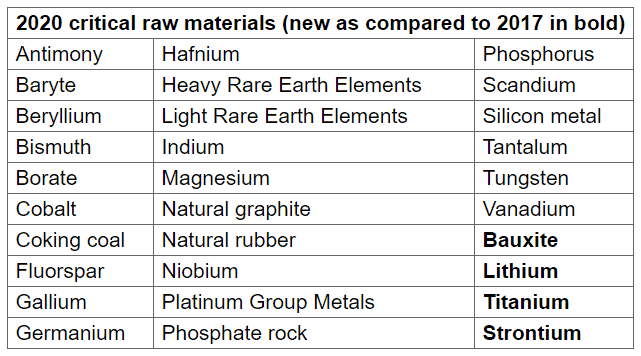
List of CRMs :
First list – the first list of CRMs was published in 2011 with 14 CRMs.
Second list – a first revised list (ie., second list) was published in 2014 with 20 CRMs.
The third list – a third list was published in 2017 with 27 CRMs.
The fourth list – a fourth list was published in 2020 with 30 CRMs.
The 2020 EU list contains 30 materials as compared to 14 materials in 2011, 20 materials in 2014, and 27 materials in 2017. 26 materials stay on the list. Bauxite, lithium, titanium, and strontium are added to the list for the first time. Helium remains a concern as far as supply concentration is concerned but disappears from the 2020 critical list due to a decline in its economic importance. The Commission will continue to monitor helium closely, because of its relevance for a range of emerging digital applications. It will also monitor nickel, given developments relating to growth in demand for battery storage.
How APA Engineering can help
Aiding businesses for more than 20 years, APA engineering has robust hybrid solutions, comprising software MDS Xpress and services for Cut cost and automate IMDS submission, automate end to end IMDS submission, automate IMDS tree structure analysis and reduce time, automate IMDS submissions, and achieve cost savings
Come and be a part of thousands of happy businesses with managed solutions for regulatory compliance reporting that trusted APA Engineering. Contact us today to learn more about robust solutions in detail.
If this regulation is applicable to you and you are interested in knowing more about this topic and available solutions, then schedule a free consult with our experts.

